Creating Own Exceptions in Java
The Java programming language allow us to create our own exception classes which are basically subclasses built-in class Exception.
To create our own exception class simply create a class as a subclass of built-in Exception class.
We may create constructor in the user-defined exception class and pass a string to Exception class constructor using super(). We can use getMessage() method to access the string.
Let's look at the following Java code that illustrates the creation of user-defined exception.
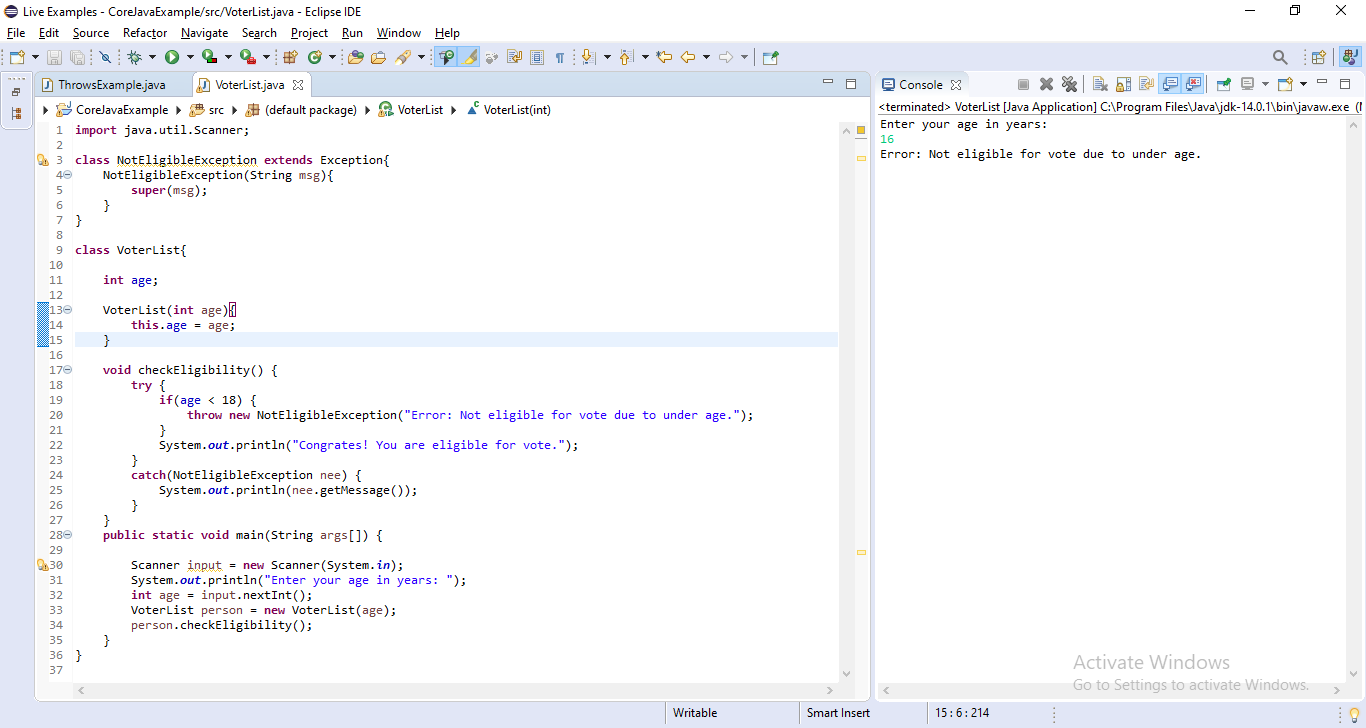
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
class NotEligibleException extends Exception{
NotEligibleException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
class VoterList{
int age;
VoterList(int age){
this.age = age;
}
void checkEligibility() {
try {
if(age < 18) {
throw new NotEligibleException("Error: Not eligible for vote due to under age.");
}
System.out.println("Congrates! You are eligible for vote.");
}
catch(NotEligibleException nee) {
System.out.println(nee.getMessage());
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your age in years: ");
int age = input.nextInt();
VoterList person = new VoterList(age);
person.checkEligibility();
}
}When we run this code, it produce the following output.